Amazon SQS
Events can be sent to an Amazon SQS queue using the amazonSqs sink type.
Like all Sinks, SQS queues can be created in the Stream Portal...
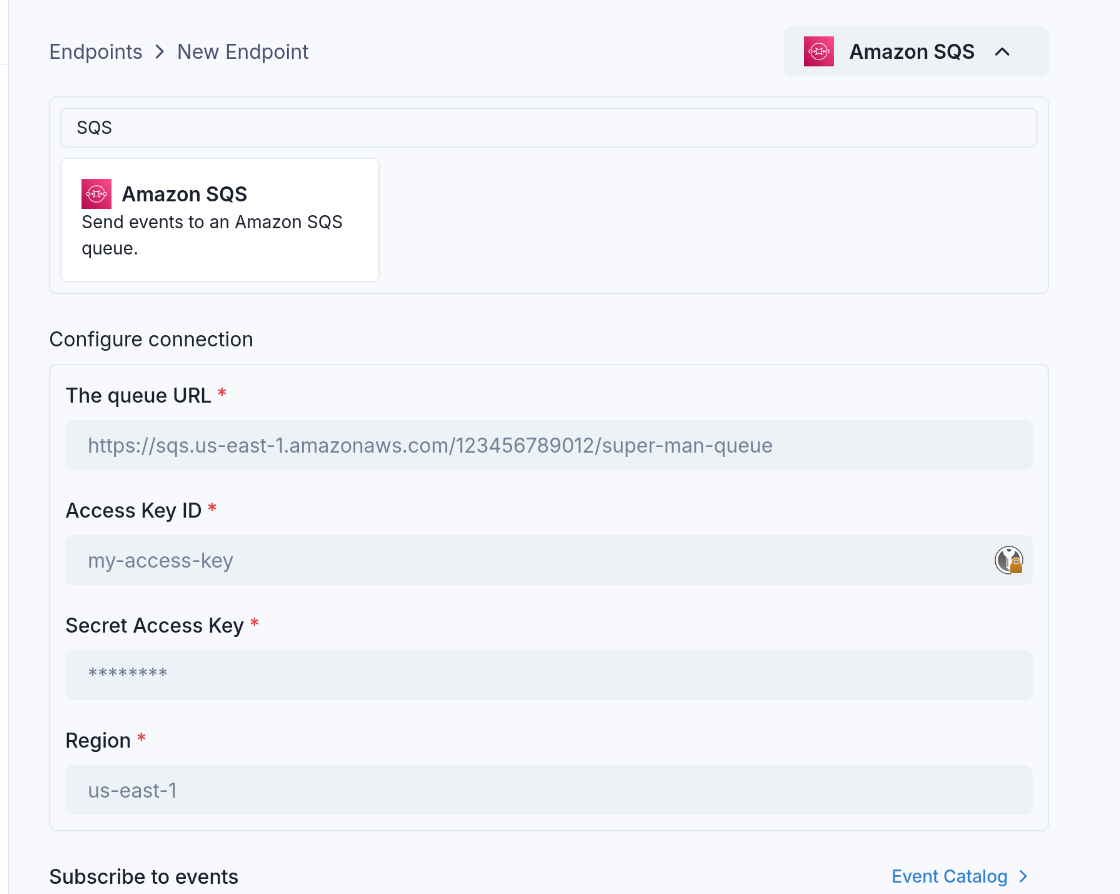
... or in the API.
curl -X 'POST' 'https://api.svix.com/api/v1/stream/strm_30XKA2tCdjHue2qLkTgc0/sink' \
-H 'Authorization: Bearer AUTH_TOKEN' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"type": "amazonSqs",
"config": {
"queueUrl": "https://sqs.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/123456789012/my-queue",
"region": "us-west-2",
"accessKeyId": "xxx",
"secretAccessKey": "xxx"
},
"uid": "unique-identifier",
"status": "enabled",
"batchSize": 100,
"maxWaitSecs": 300,
"eventTypes": [],
"metadata": {}
}'
Each event will be sent as individual messages to your SQS queue.
Transformations
By default, all amazonSqs Sinks come bundled with the following transformation code.
/**
* @param input - The input object
* @param input.events - The array of events in the batch. The number of events in the batch is capped by the Sink's batch size.
* @param input.events[].payload - The message payload (string or JSON).
* @param input.events[].eventType - The message event type (string).
*
* @returns Object containing the response.
* @returns returns.messages - The array of SQS messages to send to the SQS queue.
* @returns returns.messages[].payload - The payload of the message (string).
*/
function handler(input) {
const messages = input.events.map((event) => ({
payload: event,
}));
return {
messages,
};
}
input.events matches the events sent in create_events.
messages contains the array of SQS messages that will be sent to the queue. Each message in the array will be sent as a separate SQS message with the specified payload.
For example, if the following events are written to the stream:
curl -X 'POST' \
'https://api.svix.com/api/v1/stream/{stream_id}/events' \
-H 'Authorization: Bearer AUTH_TOKEN' \
-H 'Accept: application/json' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"events": [
{
"eventType": "user.created",
"payload": "{\"email\": \"joe@enterprise.io\"}"
},
{
"eventType": "user.login",
"payload": "{\"id\": 12, \"timestamp\": \"2025-07-21T14:23:17.861Z\"}"
}
]
}'
The default transformation code would result in two separate messages being sent to your SQS queue:
Message 1:
{
"eventType": "user.created",
"payload": "{\"email\": \"joe@enterprise.io\"}"
}
Message 2:
{
"eventType": "user.login",
"payload": "{\"id\": 12, \"timestamp\": \"2025-07-21T14:23:17.861Z\"}"
}
If you want to control the message format more precisely, you can customize the payload in each message.
For example, the following transformation code would include both the payload and event type:
function handler(input) {
const messages = input.events.map((event) => ({
payload: JSON.stringify({
payload: event.payload,
eventType: event.eventType
}),
}));
return {
messages,
};
}
This would result in the following messages being sent to your SQS queue:
Message 1:
{"payload":{"email":"joe@enterprise.io"},"eventType":"user.created"}
Message 2:
{"payload":{"id":12,"timestamp":"2025-07-21T14:23:17.861Z"},"eventType":"user.login"}